We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
If you are entering the domain of Risk Management, then you need to understand the critical differences of Hazard vs Risk. Understanding their differences will help you and your organisation comply with regulations and enhance operational resilience.
This distinction is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent accidents and injuries, guiding professionals in identifying dangers, implementing measures to mitigate the potential for harm, and ensuring safety in various environments. Read this blog ahead to learn more about the critical differences between Hazard vs Risk.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Hazard?
2) What is a Risk?
3) Key differences between Risk and Hazard
4) Advantages and disadvantages of Hazard
5) Advantages and disadvantages of Risk
6) Conclusion
What is a Hazard?
A Hazard is a situation, condition, or object that has the potential to cause harm, loss, or damage to life, health, property, or the environment. It represents a source of potential injury, illness, or adverse impact, which can arise from various sources, including natural events, technological processes, human activities, and social circumstances.
Hazards can be categorised into different types, such as physical (e.g., earthquakes, floods), chemical (e.g., toxic substances, explosives), biological (e.g., pathogens, allergens), ergonomic (e.g., repetitive strain, poor posture), and psychosocial (e.g., stress, violence). The severity and likelihood of the harm that a Hazard can cause vary widely, depending on factors such as the nature of the Hazard, the environment in which it occurs, and the vulnerability of those exposed to it.
Identifying and assessing Hazards is a critical step in Risk management, aiming to minimise or eliminate the Risks associated with these Hazards through preventive measures, preparedness, and effective response strategies. Ultimately, understanding and mitigating Hazards is essential for protecting public health and safety, preserving the environment, and ensuring sustainable development and quality of life.
What is a Risk?
Risk refers to the possibility of experiencing harm, loss, or adverse effects resulting from exposure to Hazards. It is a concept that quantifies the likelihood and potential severity of adverse outcomes arising from a particular situation or action. Understanding Risk involves considering several vital aspects:
a) Probability of occurrence: This measures how likely a Hazard will lead to a harmful event. Higher probabilities indicate more significant Risks.
b) Severity of impact: This assesses the potential extent of damage or harm that could result from the Risk. Impacts can range from minor to catastrophic.
c) Exposure: This involves considering who or what may be affected by the Risk and how. It includes identifying vulnerable populations, valuable assets, and critical systems.
d) Mitigation measures: These are strategies and actions taken to reduce the probability of occurrence or the severity of the impact, thereby managing or lowering the overall Risk.
Risks can be inherent in various activities, environments, and processes, from everyday decisions and business operations to natural disasters and technological systems. Effective Risk management involves identifying potential Risks, assessing their magnitude, implementing measures to mitigate them, and preparing for possible outcomes.
Take the first step towards ensuring workplace safety and compliance – register now for our NEBOSH Award in Health and Safety at Work Course!
Key differences between Risk and Hazard
Here's a comparison of the critical differences between Risk and Hazard in a tabular format:
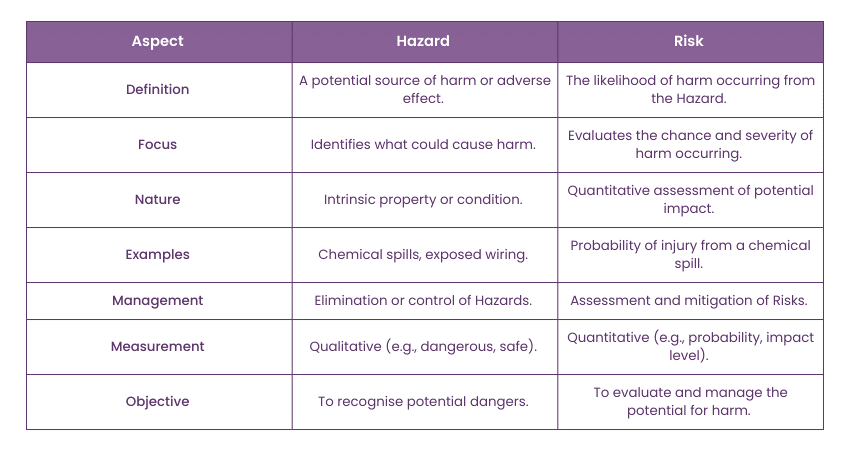
Understanding the differences between Hazard vs Risk is fundamental for implementing effective safety measures and Risk Management practices. By accurately identifying Hazards and assessing associated Risks, organisations can protect individuals, comply with regulations, and enhance operational resilience. Here are some key differences:
Nature and definition
A potential source of harm or adverse effect is called a Hazard. It also refers to any substance, process, action, or condition that can cause injury, illness, or death. Risk is the likelihood and severity of the harm that the Hazard could cause. It combines the probability of an event occurring with the consequences of that event.
Focus
Hazard concentrates on identifying what could cause harm without considering the likelihood of occurrence; on the other hand, Risk evaluates the chance (probability) and impact (severity) of harm occurring due to exposure to a Hazard.
Assessment
Hazard involves identifying and understanding the intrinsic properties of Hazards that could lead to harm; on the contrary, Risk requires assessing how likely it is that the Hazard will lead to damage and how severe that harm would be.
Management approach
Hazard aims to eliminate, reduce, or control the Hazard itself to prevent potential harm. In contrast, Risk focuses on mitigating the likelihood of the Hazard causing harm or minimising the impact of potential harm.
Examples
Hazards include chemical spills, exposed electrical wiring, and slippery floors. On the other hand, Risk involves the probability of someone getting injured by slipping on the floor or the likelihood of health issues arising from chemical exposure.
Measurement
Hazard can be typically described qualitatively (e.g., toxic, explosive) based on its inherent properties. On the contrary, Risk is often quantified through statistical analysis, measuring both the likelihood of occurrence and the severity of consequences.
Objective
Hazard recognises and understands the inherent dangers present in materials, environments, or processes; on the other hand, Risk refers to evaluating, prioritising, and managing the potential for harm, aiming to make informed decisions about safety measures and resource allocation.
Do you want to develop a strong foundation in Health and Safety? Then join us for our NEBOSH National General Certificate in Occupational Health and Safety Training!
Advantages and disadvantages of Hazard
Discussing the advantages and disadvantages of a Hazard is somewhat unconventional since Hazards are typically seen as unfavourable. However, one can consider the broader implications, including how the recognition and management of Hazards can lead to positive outcomes and the inherent drawbacks of Hazards themselves.
Advantages of recognising and managing Hazards
Here are some advantages of recognising and managing Hazards:
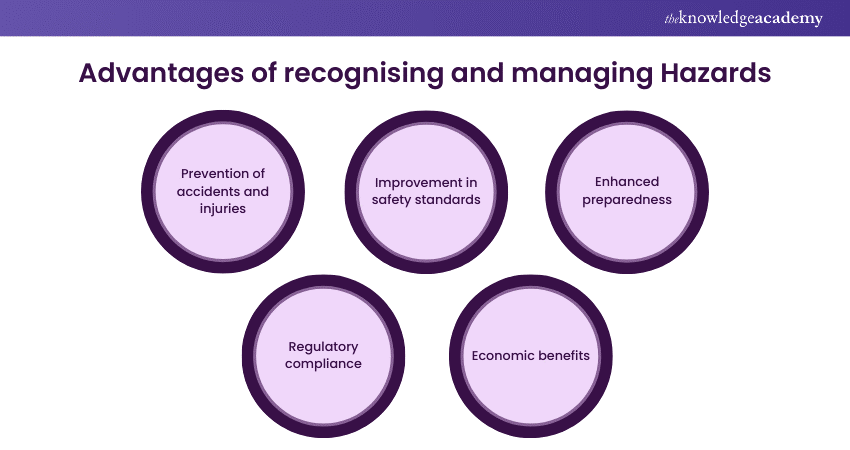
a) Prevention of accidents and injuries: Identifying Hazards allows for implementing control measures to prevent accidents and injuries, enhancing safety for individuals and communities.
b) Improvement in safety standards: Recognising Hazards leads to improved safety protocols and standards, promoting a culture of safety in workplaces and public spaces.
c) Enhanced preparedness: Understanding potential Hazards enables better preparedness for emergencies, minimising the impact of adverse events.
d) Regulatory compliance: Identifying and managing Hazards is essential for compliance with health and safety regulations, helping to avoid legal issues and financial penalties.
e) Economic benefits: By preventing accidents and injuries, Hazard management can lead to cost savings for businesses and society by reducing healthcare costs and improving productivity.
Disadvantages of Hazards
Let’s look at some disadvantages of Hazards:
a) Risk of harm: Hazards inherently pose a Risk to people, property, and the environment, which can lead to injuries, fatalities, and ecological damage.
b) Economic costs: The presence of Hazards can result in significant financial costs, including repair and litigation costs, increased insurance premiums, and loss of business.
c) Psychological impact: Exposure to Hazards can cause stress, anxiety, and fear among individuals, affecting mental health and well-being.
d) Resource allocation: Managing Hazards requires allocating resources, such as time, money, and personnel, which might be limited or used for other purposes.
e) Limitations on activities: In some cases, Hazards may restrict certain activities or operations, impacting productivity and innovation.
Boost your incident investigation skills with our NEBOSH HSE Introduction to Incident Investigation Training!
Advantages and disadvantages of Risk
Discussing the advantages and disadvantages of Risk involves acknowledging that while Risk often implies potential adverse outcomes, the concept of Risk itself can lead to positive developments when managed appropriately.
Advantages of engaging with Risk
Here are some advantages of engaging with Risk:
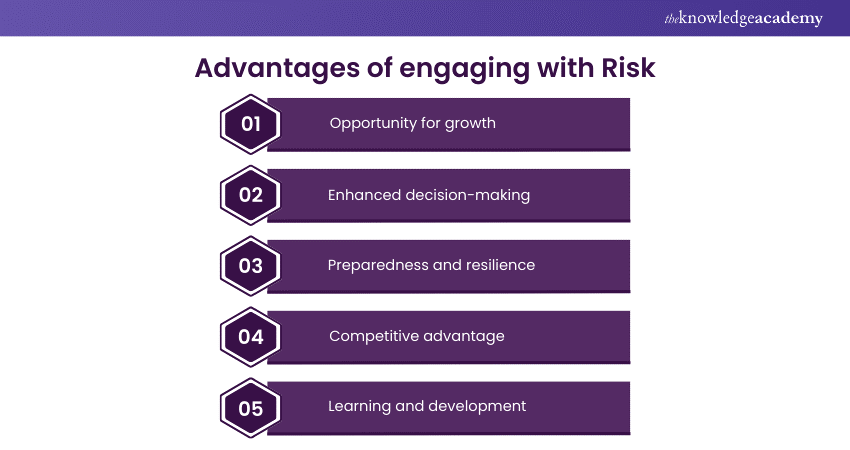
a) Opportunity for growth: Taking calculated Risks can lead to new opportunities, innovation, and development. Businesses and individuals often need to embrace some level of Risk to achieve significant rewards.
b) Enhanced decision-making: Understanding and analysing Risks improves decision-making processes, allowing for more informed choices that balance potential rewards against possible dangers.
c) Preparedness and resilience: Identifying and assessing Risks enable better preparedness for unforeseen events, building resilience in organisations, communities, and individuals.
d) Competitive advantage: In a business context, effectively managing Risk can provide a competitive advantage by navigating uncertainties more successfully than competitors.
e) Learning and development: Encountering and managing Risks can lead to valuable learning experiences, fostering adaptability and problem-solving skills.
Disadvantages of Risk
Here are some disadvantages of Risk:
a) Potential for loss: Engaging with Risk carries significant losses, affecting finances, health, safety, and reputation.
b) Uncertainty and stress: Dealing with Risk can introduce uncertainty and anxiety, impacting mental well-being and leading to decision paralysis in some cases.
c) Resource allocation: Assessing and mitigating Risks requires resources, which could be allocated elsewhere, potentially leading to missed opportunities.
d) Overcautious behaviour: A heightened focus on Risk might lead to overly cautious behaviour, stifling innovation and growth.
e) Failure and setbacks: Not all Risks pay off; failure to manage Risks effectively can lead to setbacks, failures, and sometimes catastrophic consequences.
Promote workplace wellbeing and enhance productivity with our NEBOSH Working with Wellbeing Training – join now!
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between Hazard vs Risk is crucial for effective safety management. While Hazards represent potential sources of harm, Risk evaluates the likelihood and severity of these Hazards causing actual damage. This differentiation aids in implementing targeted measures, ensuring a safer environment by minimising potential threats and their impacts.
Empower your Risk Management skills with our NEBOSH HSE Award in Managing Risks and Risk Assessment at Work Training – register now!
Frequently Asked Questions
A Hazard becomes a risk when its potential for harm intersects with exposure or circumstances that increase the likelihood of that harm occurring. The transformation involves assessing the Hazard's inherent danger and the specific conditions under which it could lead to adverse outcomes, thereby creating a Risk.
Hazard vs. Risk is based on distinguishing between the potential source of harm (hazard) and the likelihood of the damage occurring (Risk). This differentiation is essential for effectively managing safety by identifying dangers and assessing how likely they are to cause adverse outcomes, enabling targeted preventive measures and Risk mitigation strategies.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various NEBOSH Courses , including NEBOSH Award in Health and Safety at Work, NEBOSH International General Certificate in Occupational Health and Safety Training, and NEBOSH HSE Award in Managing Risks and Risk Assessment at Work Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Health and Safety Hazards methodologies.
Our Health & Safety blogs covers a range of topics related to Safety, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Health and Safety skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
Mon 18th Mar 2024
Tue 7th May 2024
Mon 24th Jun 2024
Mon 16th Sep 2024
Mon 25th Nov 2024
 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course.png)